Clamping Battery Telemetry for 1 or 2 strain gages channels
- Clamps to any shaft 25 mm or larger
- Small Package
- 2 strain gauge bridge channels
- Up to 48 hours of battery life
- Lightweight rugged IP67 housing
- Digital 2.4 GHz RF link for reliable transmission without interference or spikes
- Programmable gain
Introduction
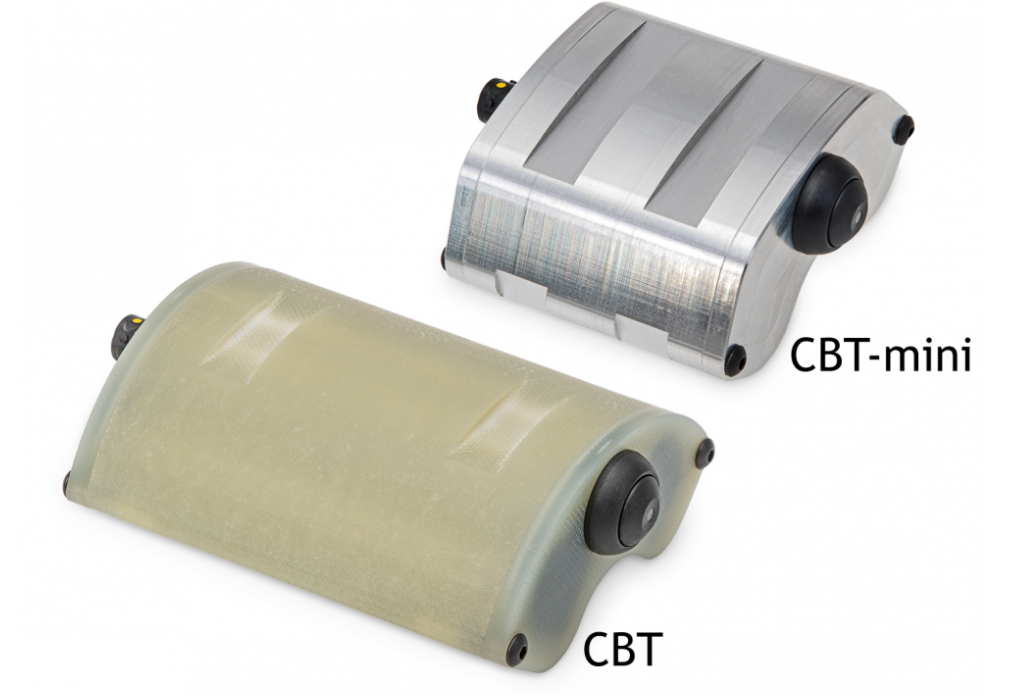
The Michigan Scientific Clamping Battery Telemetry (CBT) is a wireless, battery powered, signal transmitter for strain gauges that easily mounts to shafts with a minimum diameter of 25 mm, making it ideal for shaft mounting and very versatile. The Michigan Scientific Telemetry provides reliable signal transmission without interference or signal spikes.
Specifications
| CBT - 320 | |
|---|---|
| RF Frequency Range | 2.4 GHz |
| Channel Type | Strain Gauge, Full Bridge, 350 Ω or higher |
| Channel Count | 1 or 2 |
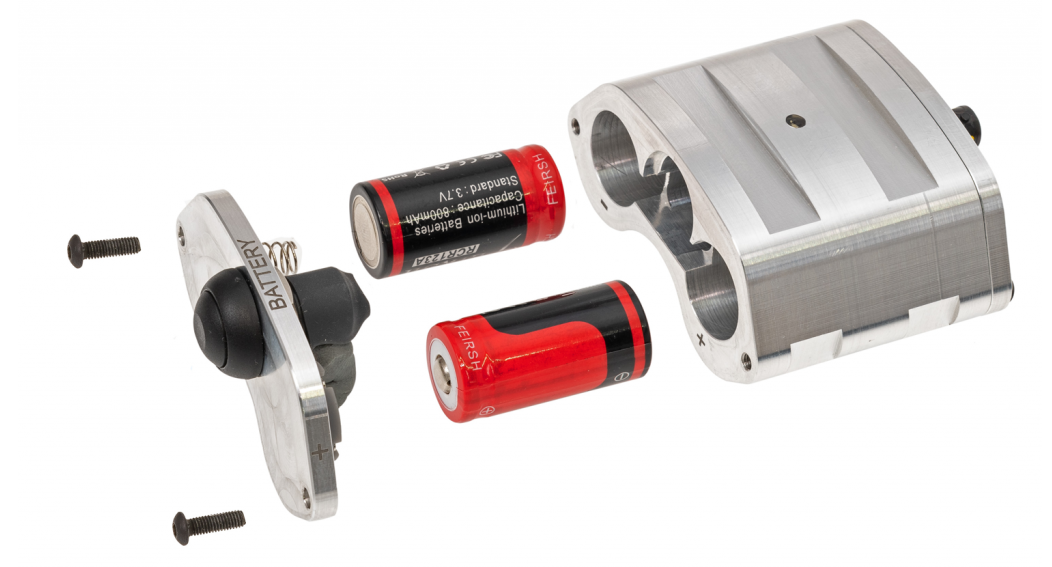
| Battery Type | Two 18650 Rechargeable lithium batteries |
| Continuous Battery Life | 48 hours for 1 strain gauge bridge. 36 hours for two strain gauge bridges |
| Weight | 140 grams (235 grams with batteries installed) |
| Gain Type | Programmable gain via USB |
| Input Type | 0.1 to 10 mV/V |
| Shunt | Resistor Fixed 100 kΩ standard, other shunt resistor values available |
| Typical Broadcast Distance | 1-2 meters, line of sight |
| Channel Sampling Rate | 3 kHz |
| Signal Output | ± 10 Volt Analog |
| System Resolution | 12 Bit |
| Operating Temperature | -20°C to +50°C (battery temperature limit) |
| Power Requirement | 9 to 36 VDC, 4.5 Watts |
| Total System Delay | < 670 μs |
| RF Channels Available | 16 |
Installation
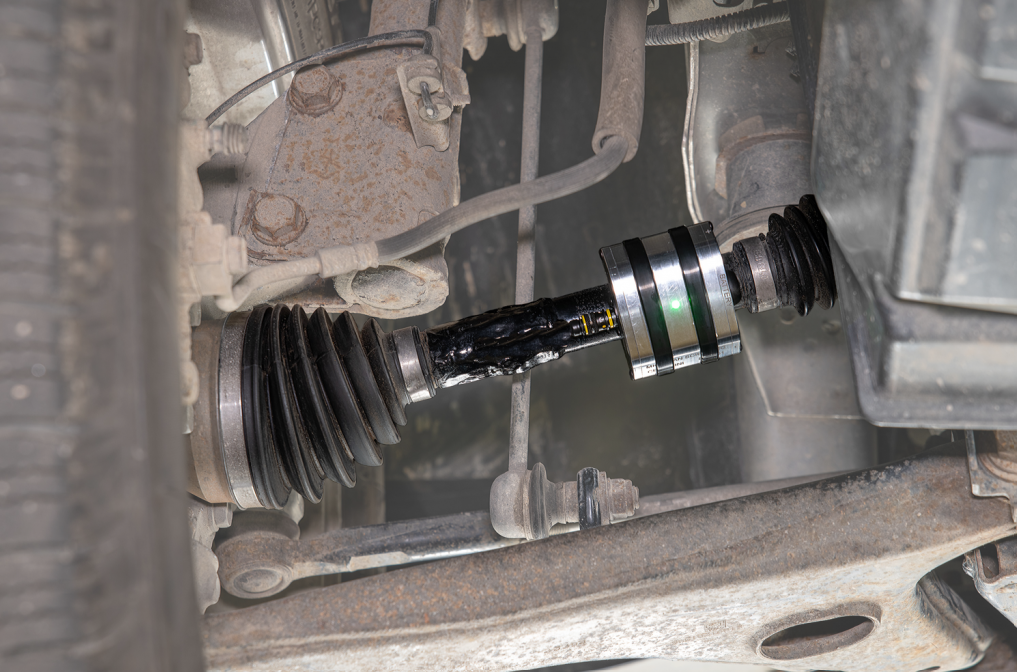
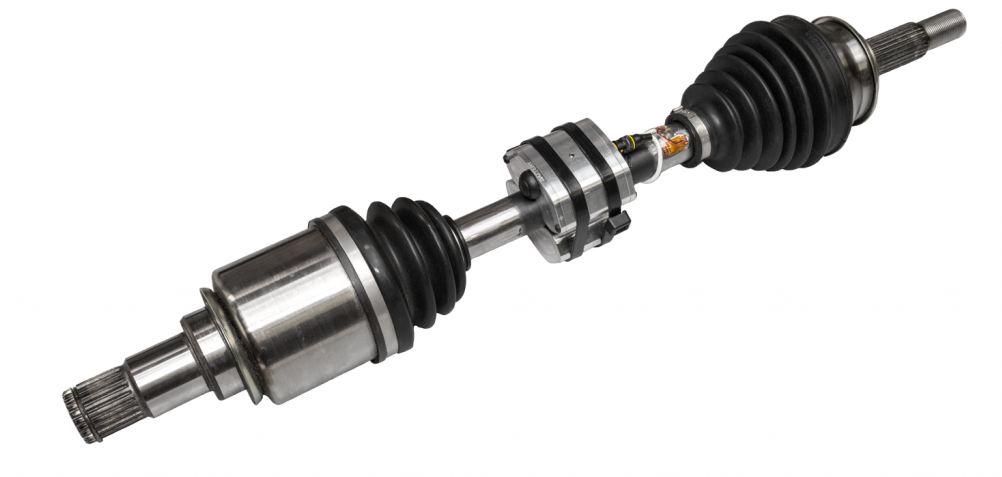
The CBT can conveniently be strapped to any shaft with load rated plastic zip ties, steel banding, or hose clamps. The CBT provides excitation and signal conditioning to the strain gauges, then digitally transmits the signals via RF in the 2.4 GHz broadcast frequency range.
For higher speed shafts when shaft balancing is required a counter weight can be purchased and should be mounted 180 degrees opposite the CBT. The CBT is a small rugged housing and is designed for hostile environments.
Applications

- Input signal type
- SG bridge
- Input channels
- 1 , 2
- Tension d'alimentation
- Batteries
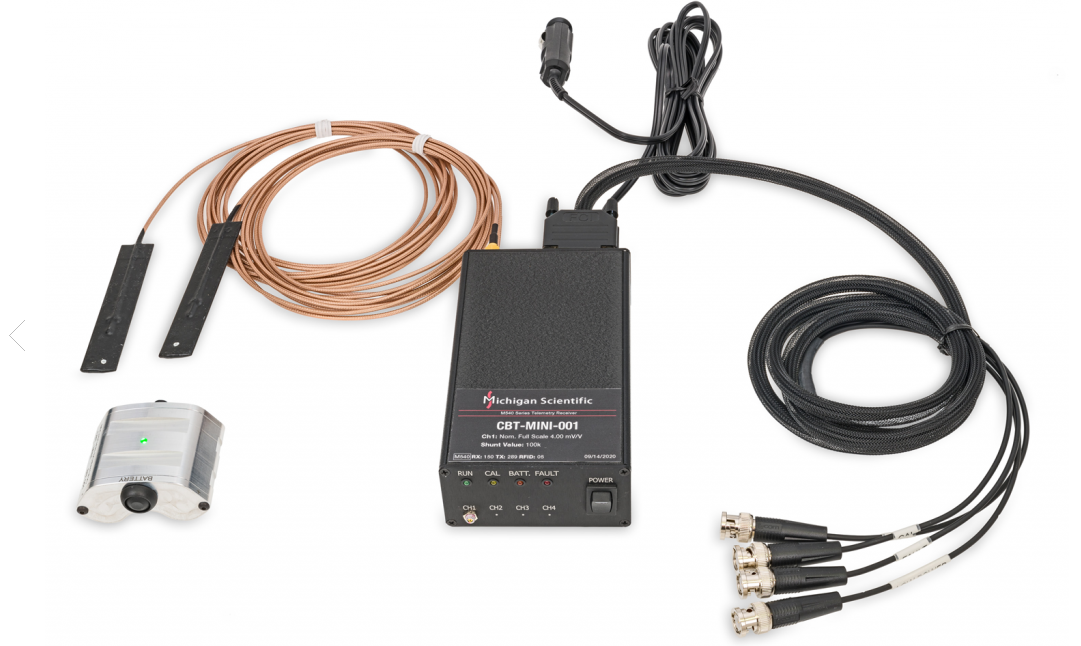
Receiver
- Geometry
- Number of channels
- Counterweight
- Batteries
Produits associés

Series 320

540 Series

CIT